Image Similarity
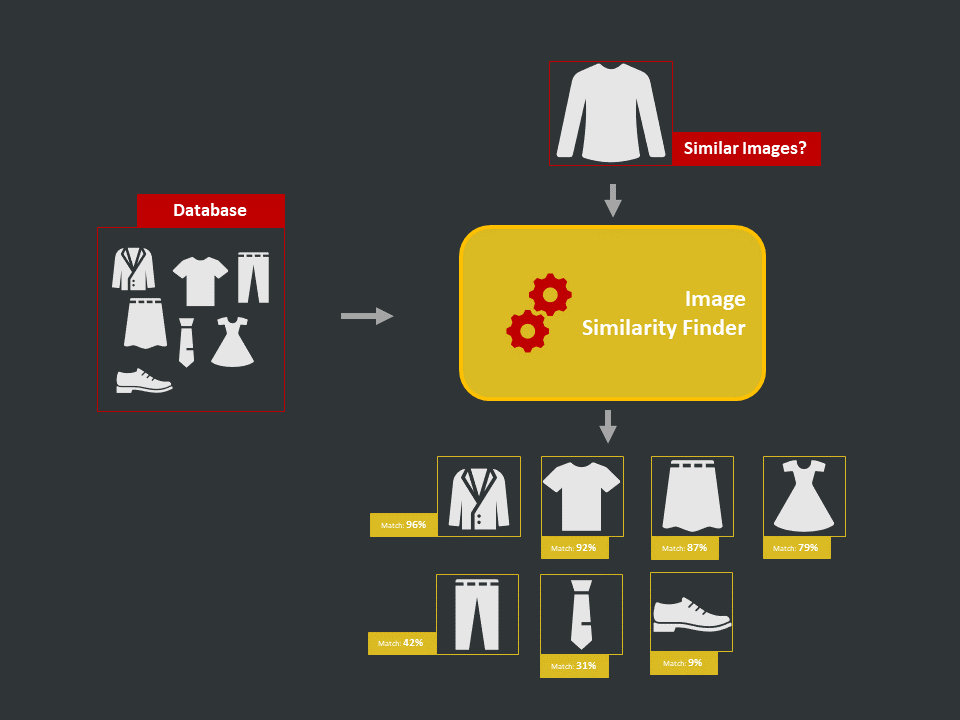
Introduction
- Definition: Image similarity is the measure of how similar two images are. In other words, it quantifies the degree of similarity between intensity patterns in two images.
- Applications: Duplicate product detection, image clustering, visual search, product recommendations.
- Scope: Fine-tuning on classes for greater accuracy
- Tools: TFHub
Models
DeepRank
DeepRank: A New Deep Architecture for Relevance Ranking in Information Retrieval. arXiv, 2017.
ConvNets
Pre-trained models like MobileNet, EfficientNet, BiT-L/BiT-M can be used to convert images into vectors. These models can be found on TFHub. For more accuracy, fine-tuning can be done.
FAISS
Billion-scale similarity search with GPUs. arXiv, 2017.
Faiss is a library for efficient similarity search and clustering of dense vectors.
Siamese Network
Siamese network is a neural network that contains two or more identical subnetwork. The purpose of this network is to find the similarity or comparing the relationship between two comparable things. Unlike the classification task that uses cross-entropy as the loss function, the siamese network usually uses contrastive loss or triplet loss.
Similarity Measures
L1 (Manhattan distance), L2 (Euclidean distance), Hinge Loss for Triplets.
Process flow
Step 1: Collect Images
Download the raw image dataset into a directory. Categorize these images into their respective category directories. Make sure that images are of the same type, JPEG recommended. We will also process the metadata and store it in a serialized file, CSV recommended.
Step 2: Encoder Fine-tuning
Download the pre-trained image model and add two additional layers on top of that: the first layer is a feature vector layer and the second layer is the classification layer. We will only train these 2 layers on our data and after training, we will select the feature vector layer as the output of our fine-tuned encoder. After fine-tuning the model, we will save the feature extractor for later use.
Step 3: Image Vectorization
Now, we will use the encoder (prepared in step 2) to encode the images (prepared in step 1). We will save the feature vector of each image as an array in a directory. After processing, we will save these embeddings for later use.
Step 4: Metadata and Indexing
We will assign a unique id to each image and create dictionaries to locate information of this image: 1) Image id to Image name dictionary, 2) Image id to image feature vector dictionary, and 3) (optional) Image id to metadata product id dictionary. We will also create an image id to image feature vector indexing. Then we will save these dictionaries and index objects for later use.
Step 5: UAT Testing
Wrap the model inference engine in API for client testing. We will receive an image from user, encode it with our image encoder, find Top-K similar vectors using Indexing object, and retrieve the image (and metadata) using dictionaries. We send these images (and metadata) back to the user.
Step 6: Deployment
Deploy the model on cloud or edge as per the requirement.
Step 7: Documentation
Prepare the documentation and transfer all assets to the client.
Use Cases
Multi-endpoint API Similarity System
The task was to build an API that will support multiple endpoints. Each endpoint supports a separate similarity system. We built 2 endpoints: endpoint 1 would find tok-K most similar fashion images and endpoint 2 would find top-K most similar food images. Checkout the notion here.
Beanstalk Image Similarity System
There are 2 endpoints in the API - one for training and the other for inference. During training, the system will receive a zipped file of images. At the time of inference, this trained system would receive an image over inference endpoint and send back top-K most similar images with a confidence score. The API was deployed on AWS beanstalk. Checkout the notion here.
Image + Text Similarity
Use the textual details and images of products, find the exact similar product among different groups. Around 35 GB of retail product images was scraped and used to build the system. Checkout the notion here.
Siamese Network Image Similarity on MNIST
Siamese networks are incredibly powerful networks, responsible for significant increases in face recognition, signature verification, and prescription pill identification applications. The objective was to build image pairs for the siamese network, train the siamese network with TF Keras, and then compare image similarity with this siamese network.
Visual Recommendation
Use image similarity to recommend users visually similar products based on what they searched. Checkout the notion here.